From apps using Generative AI to create digital artwork or online vector editing softwares generating graphics from flat sketches to Adidas automated Speedfactory that utilises robotic arms, laser cutting, and 3D printing to make running shoes, AI is unlocking opportunities, driving efficiency, and fostering creativity and innovation. Let us examine how the implementation of AI affects the dynamics of the fashion value chain.

With 73% of fashion companies planning to increase AI investments this year per Statistica, AI’s influence is visible in every aspect of the value chain. Similar to the evolution of the IT infrastructure two decades back, the fashion industry is experiencing a renaissance with the integration of AI across the value chain.
From algorithm-based design production and stock management to trend forecasting and hyper-personalised marketing, AI is evolving time-honoured industry conventions. For individuals in fashion design, investment or operations, understanding what the fashion industry should prioritise to stay ahead of AI-influenced consumer behaviour is crucial.
Fashion today faces intense pressure: speeding up trend cycles, reducing waste, keeping customers inspired with search-and-shop, and doing it all for a profit. AI is stepping in as a game-changer – enabling hyper‑personalisation, smart trend forecasting, and sustainable operations. In this article, we explore how artificial intelligence is reshaping the industry, with case studies highlighting its impact at each stage of the value chain.
RELATED ARTICLES
Top beauty apps you’ll want to download now
Trend Forecast
The implementation of AI in trend prediction enables businesses to analyse vast amounts of data quickly, uncover patterns, and forecast future market movements with precision. By automating data-driven insights, AI helps companies stay ahead of consumer preferences, adapt to changes in real-time, and make informed decisions, leading to effective product development, targeted marketing strategies, and competitive advantage.
Predictive analytics is used by 60% fashion brands to forecast trends, per Business of Fashion. For example, Zara incorporated AI into its operations to enhance trend forecasting, stock management, and inventory control. The fast fashion giant employs AI technologies to identify emerging fashion trends based on analyzing social media posts, influencer activity, and customer interactions on their website. Zara algorithms spot popular styles, colours, and patterns that are gaining traction among consumers and what once took months to analyze and forecast, Zara now achieves in minutes.
H&M, another giant in fashion retail, embraced AI to streamline its trend forecasting. AI algorithms monitor the images shared on social media by fashion influencers and consumers, identifying emerging colours, patterns, and styles. H&M also reviews customer purchase behaviour, browsing habits, and online interactions, enabling the brand to predict what consumers are likely to buy next.
Design and Product Development
AI’s impact on fashion begins on the design board, where it enhances creativity and accelerates product development. Fashion brands increasingly rely on AI algorithms to predict trends, create designs, and develop fabrics. Repsketch, for example, is an online vector editing software that generates graphics from flat sketches. It allows fashion designers to change the background and add material specifications. Such realistic visuals can give the fashion team a glimpse of the final product before the production of physical samples, reducing the number of iterations throughout the sample creation process. Images generated by AI can be used for presentations to retailers and customers.

Artiphoria is another example of using Generative AI to create digital artwork. It allows users without graphic design skills to make graphics with a single click. It is an excellent tool for creating artwork that can be printed on apparel and accessories. Luxury fashion brand Gucci uses AI-driven tools like IBM’s Watson to analyse consumer preferences and suggest designs that will appeal to their target audience. This integration of technology in the design process allows Gucci to keep pace with the market and lead it by anticipating shifts in consumer tastes with greater precision.
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data helps fashion designers to explore new styles, colour palettes, and silhouettes, which can be tested digitally before production of physical samples, significantly reducing waste and enhancing sustainability. Fast fashion giant H&M uses AI to sort used garments and predict fabric lifespan, enabling informed circular design practices. Adidas integrates AI into its sustainability initiatives by assisting in developing sustainable materials and optimising production techniques to reduce waste. AI algorithms help in selecting low-carbon materials, designing recyclable products, and implementing circular economy principles.
Production Process
AI’s role in fashion production has been transformative, streamlining production processes and optimising operations. Leading fashion retailers like H&M have embraced AI-driven automation in their production lines to increase efficiency. AI-powered machines can now automate tasks such as stitching, fabric cutting, and quality control. One of the most notable examples is Adidas, which has introduced a fully automated “Speedfactory” in Germany, where robots and AI work together to manufacture products on demand. This speeds up production cycles and enables highly customisable products, reducing the reliance on large-scale traditional manufacturing methods and minimising stock surplus.
Supply Chain Optimisation
In an industry where supply chain efficiency is paramount, AI has become a game-changer for fashion brands looking to streamline their operations. AI helps to predict demand, optimise stock levels, and improve distribution logistics. A prime example is Zara, which uses AI to predict customer demand in real-time. By analysing purchasing patterns, Zara can adjust production schedules and stock levels accordingly, ensuring that stores are always stocked with the right products in the right quantities. This ability to react swiftly to market conditions allows Zara to stay ahead of competitors and significantly reduces the costs associated with overproduction and inventory holding.
Retail and Customer Engagement
Per McKinsey: ‘The role of the store has changed: 70 percent of retail sales today are digitally influenced. Initial discovery is now typically done online. Once you see something online, the likelihood is you want to see it in the store, but that doesn’t mean you’ll purchase it there. Stores have become more experiential; they have less stock and are more about giving you a sense of the DNA of the brand.’
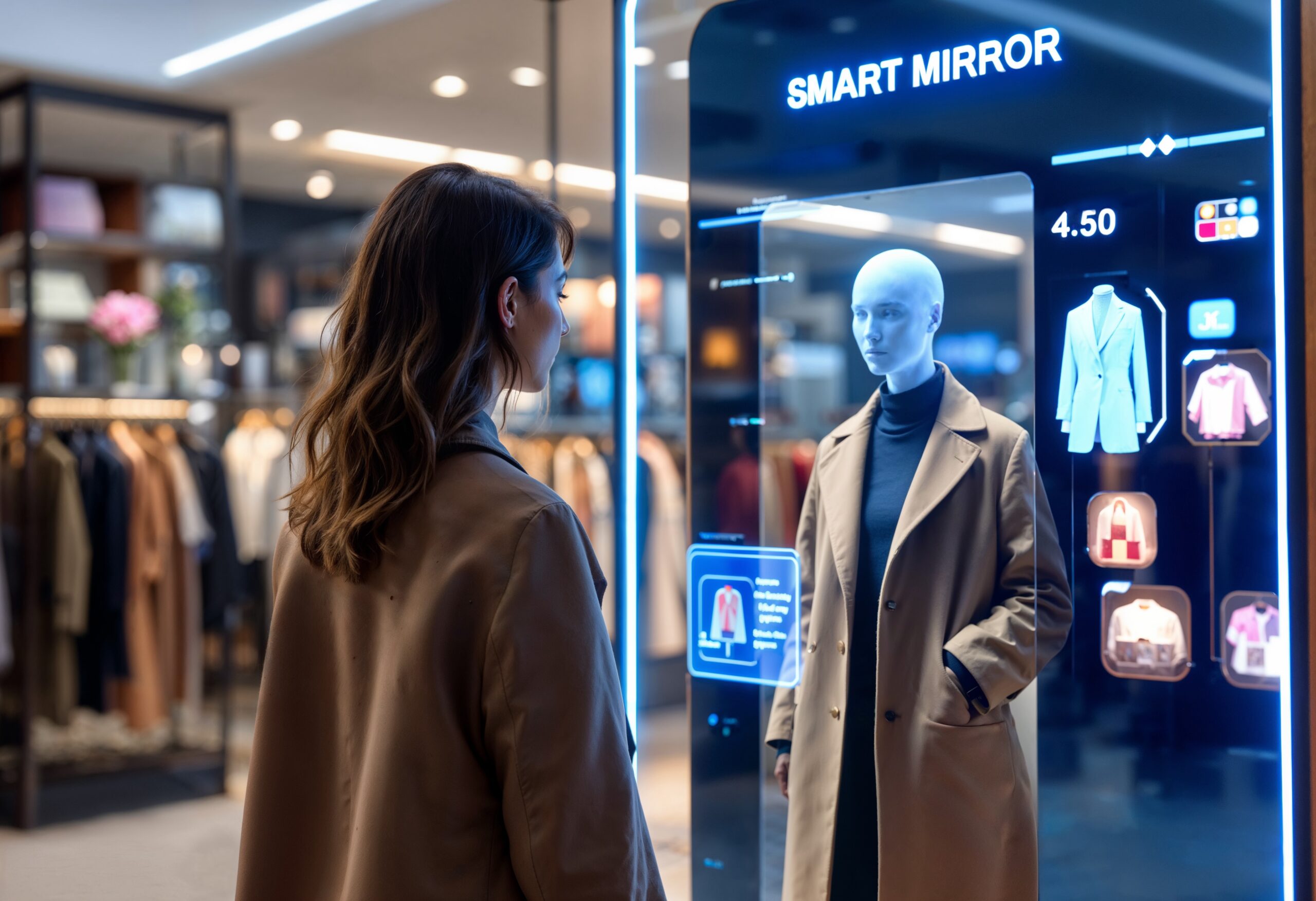

The intersection of AI and retail has allowed fashion brands to deliver personalised experiences at scale. AI technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing are being used to create tailored shopping experiences for customers, enhancing engagement and driving sales. A key example is Net-a-Porter; by analysing data from customers browsing history, preferences, and purchase patterns, it offers targeted product suggestions, increasing conversion rates and fostering loyalty. Similarly, Burberry has implemented AI-powered chatbots to enhance its customer service experience, ensuring that shoppers receive timely, hyper-personalised assistance, which is critical for maintaining relationships with consumers.
Zalando is investing in generative AI to become a one-stop. Online destination for consumers, spanning product discovery and search. Per BoF: ‘Zalando’s AI assistant, which leverages ChatGPT technology, has been used by over 500,000 customers since its launch in 2023… Zalando Stories use generative AI to show curated content to users based on real-time data. Similarly, Trend Spotter, a B2B tool, identifies emerging trends on Zalando across six fashion capitals, enabling brands to create styles and content that resonate with real-time customer preferences.’
Fitting And Visualisation
Fashion retailers are increasingly leveraging AI to enhance fitting and visualisation experiences, making shopping more personalised and efficient. A prime example is ASOS, which has integrated AI into its fitting rooms through a virtual try-on feature. Customers can upload their photos, and the system uses AI to simulate how clothes will look based on their body shape and size. This not only reduces the uncertainty of online shopping but also helps shoppers make more informed decisions, improving conversion rates and reducing return rates. Additionally, ASOS has been able to recommend sizes based on the user’s body data, further enhancing the personalised shopping experience.
Another notable example is Zara, which has adopted AI-powered visualisation technology to streamline its fitting processes. Through machine learning algorithms, Zara’s AI system can predict how different fabrics, styles, and cuts will fit a variety of body shapes. This capability extends to the brand’s online store and in-store displays, where customers can virtually “try on” clothes using augmented reality (AR). This innovation ensures that customers not only view garments from multiple angles but also see how they move and fit in real-time, contributing to a more immersive shopping experience. Zara’s use of AI is reshaping traditional fitting rooms, providing customers with a more efficient and engaging way to shop.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Sustainability is a growing concern in the fashion industry, and AI is helping fashion retailers and brands to tackle environmental challenges. By using AI to analyse production processes and consumer behaviour, companies are able to reduce waste and improve sustainability efforts. Stella McCartney, a pioneer in sustainable fashion, uses AI to track the environmental impact of its supply chain. The luxury fashion brand has partnered with H&M’s Circular Innovation Lab to explore AI-driven solutions for reducing textile waste and promoting circular fashion. AI’s ability to optimise resource usage and extend the lifecycle of garments is integral to achieving these sustainability goals, ensuring that luxury fashion brands can be both profitable and eco-conscious.
Marketing and Consumer Insights
AI’s impact on marketing strategies is visible, particularly in terms of how fashion brands engage with their customers. L’Oréal is one of the leaders in using AI to drive its marketing efforts, employing AI to analyse consumer sentiment across digital platforms. Through sentiment analysis, L’Oréal determines how different campaigns and products appeal to diverse customer demographics, allowing highly targeted advertising.
AI-driven algorithms are used to tailor content, from social media posts to email marketing campaigns, ensuring that each consumer receives relevant messages at the right time. This level of precision marketing is essential for brands to build profitable customer relationships in a crowded digital marketplace. Burberry tailors content across social media, email campaigns, and website interactions, ensuring that each customer receives messages that are in sync with their unique preferences. The AI algorithms analyse vast amounts of data, allowing the brand to promote a new collection or offer personalised recommendation.
Conclusion
AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it is actively shaping the fashion value chain today. From design and production to supply chain optimisation and customer engagement, it is driving efficiencies, sustainability, and innovation across the industry. As high-net-worth retailers, investors, and consumers continue to navigate the evolving fashion sector, understanding the practical applications of AI in this industry will be key to seizing opportunities and staying ahead of the curve. The case studies highlighted in this article demonstrate the significant impact of AI and provides a glimpse into a future where AI is integral to every aspect of fashion business operations.
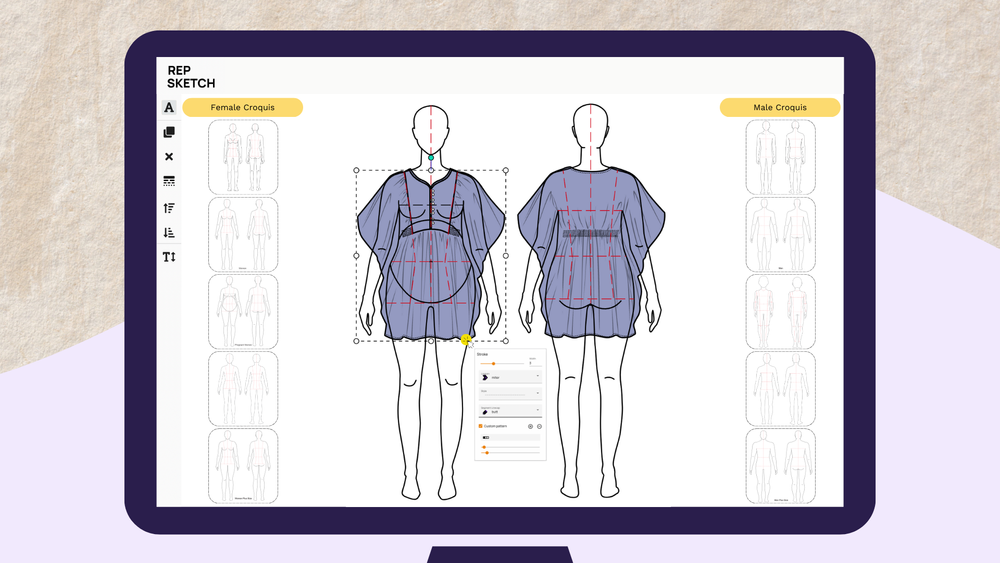
Image: RepSketch

Jasmeen Dugal is Associate Editor at FashionABC, contributing her insights on fashion, technology, and sustainability. She brings with herself more than two decades of editorial experience, working for national newspapers and luxury magazines in India.
Jasmeen Dugal has worked with exchange4media as a senior writer contributing articles on the country’s advertising and marketing movements, and then with Condenast India as Net Editor where she helmed Vogue India’s official website in terms of design, layout and daily content. Besides this, she is also an entrepreneur running her own luxury portal, Explosivefashion, which highlights the latest in luxury fashion and hospitality.